Getting started with the JavaScript SDKs
Sharetribe’s JavaScript Software Development Kit (SDK) and Integration SDK simplify interactions with our APIs. You can read more about features and functionalities in our SDK GitHub Documentation . This guide covers
- Installation
- Initialization and instantiating the SDK
- Creating a trusted SDK instance
- Example use cases
Overview
Our SDKs simplify making requests to the backend by handling authentication and providing convenient access to Sharetribe’s APIs. They allow you to interact easily with
- Marketplace API , for interacting with marketplace data where the actor is the end user
- Integration API , for building integrations within the marketplace where the actor is a server or service
- Asset Delivery API , for delivering assets
You can find more information on API usage and guidelines for choosing which to work with in this article .
There are two JavaScript SDKs you can use to access the APIs
| Sharetribe SDK | Sharetribe Integration SDK | |
|---|---|---|
| Access level | Limited to user-scope and public data | Full marketplace (operator-level) access |
| Actor | Marketplace user | Server, script, Zapier, etc. |
| API access | Marketplace API and Asset Delivery API | Integration API |
| Client credentials | Client ID, Client secret for trusted SDK instances | Client ID, Client Secret |
| Secure runtime environment needed | When initialised with a Client Secret | Yes |
Throughout this article, you’ll find that we use the term ‘Trusted SDK instance’. In practice, this means an instance of the SDK that holds a trusted user access token. This takes part after performing a token exchange, which we will cover later in this article.
To try out the SDKs, visit our Github documentation for the Sharetribe SDK and the Integration SDK for instructions on how to get started. For a more detailed guide on using the SDKs with code, keep following this tutorial.
Certain requests will a secure runtime environment. One way to do this is to run a small server from which to make these types of requests.
Installation
To get started with the SDKs, you’ll first need to install them with either Yarn or npm .
yarn
yarn add sharetribe-flex-sdk
yarn add sharetribe-flex-integration-sdkSDK Initialization Overview
Obtaining the Client ID and Client Secret
To use the Marketplace API or Integration API, you will need a Client ID from an application. You can create an application in Sharetribe Console: Build > Advanced > Applications
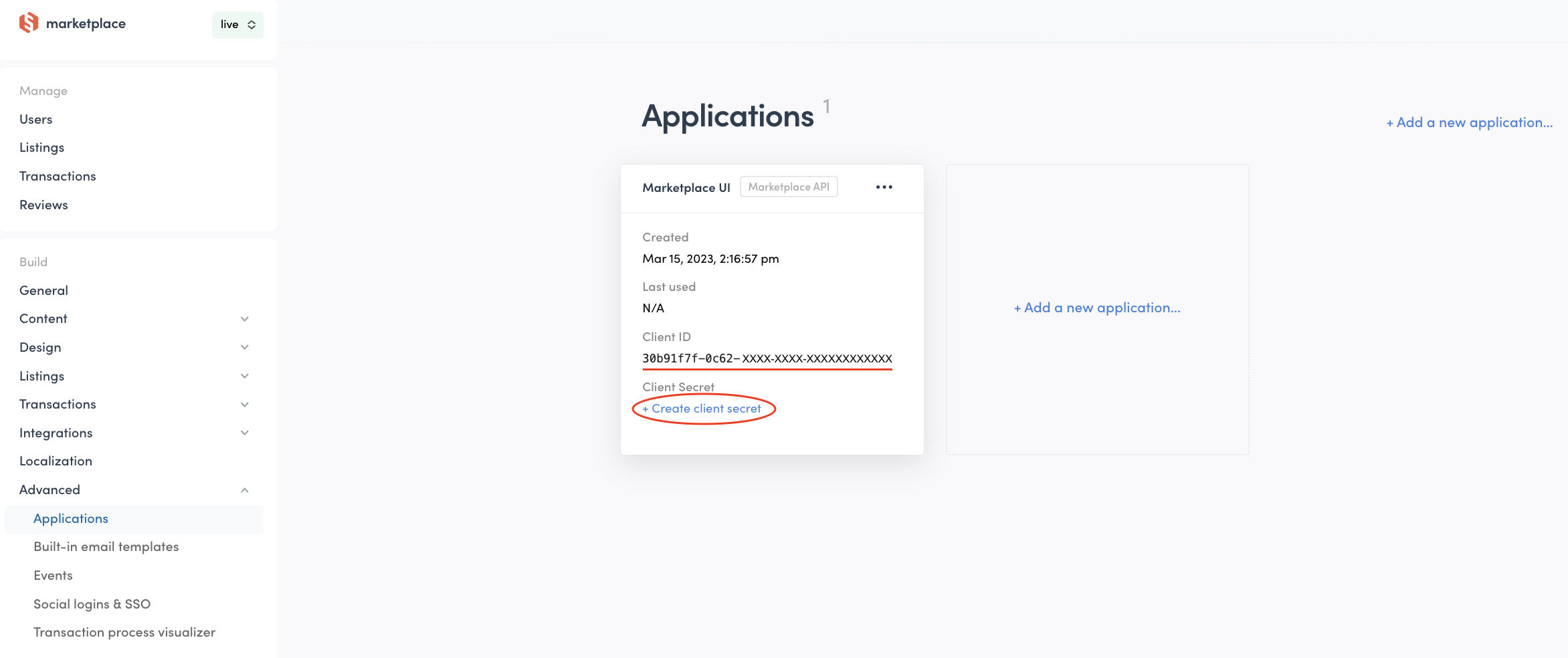
You should also make note of the Client Secret, as some requests require initializing the SDK with both the Client ID and Client Secret.
An example of this type of request is making a privileged transition in a transaction. This requires that the:
- Client ID and Client Secret are used when creating an instance of the SDK
- A token exchange happens to obtain a trusted user access token
- The request is made from a secure runtime environment, such as a server
In the Sharetribe Web Template , these types of requests are made on a small Node.js server included in the Template.
Initializing a Sharetribe SDK instance
You can initialize a Sharetribe SDK instance using only the application’s Client ID. Ensure the Client ID is from a Marketplace API application created in Console.
const sharetribeSdk = require('sharetribe-flex-sdk');
const sdk = sharetribeSdk.createInstance({
clientId: '<Client ID>',
});This will allow you to make requests that don’t require authentication e.g. querying listings.
Initializing an Integration SDK instance
If you are accessing Integration API, you’ll need to also provide the Client Secret. Ensure the Client ID is from an Integration API application created in Console.
const sharetribeIntegrationSdk = require('sharetribe-flex-integration-sdk');
const integrationSdk = sharetribeIntegrationSdk.createInstance({
clientId: '<Client ID>',
clientSecret: '<Client Secret>',
});Keep your application’s Client Secret secure. Never expose it to untrusted devices or applications such as end user browsers or mobile apps.
Initializing the Sharetribe SDK with a trusted user access token
To make certain requests, you will need to access the Marketplace API with a trusted SDK instance. In order to do this, you’ll need to log in using the SDK and perform a token exchange to retrieve a trusted token.
Create an instance of the SDK with the Client ID, Client Secret, and Token Store
const sharetribeSdk = require('sharetribe-flex-sdk');
var sdk = sharetribeSdk.createInstance({
clientId: '<Client ID>',
clientSecret: '<Client Secret>',
});Keep your application’s Client Secret secure. Never expose it to untrusted devices or applications such as end user browsers or mobile apps.
Log in using valid credentials
sdk.login({ username: '<User email>', password: '<User password>' });Exchange the user access token for a trusted user access token and create a new instance of the SDK
sdk.exchangeToken().then((res) => {
const sdkTrusted = sharetribeSdk.createInstance({
clientId: '<Client ID>',
tokenStore: sharetribeSdk.tokenStore.memoryStore(res.data),
});
});Now you can use sdkTrusted to make requests that require a trusted
user access token, e.g. deleting a user with
Marketplace API .
Requests that require a trusted user access token rely on valid login credentials appropriate for the request. For example, to delete a user you must log in with that user’s credentials.
Example usage
Here are a few examples demonstrating common uses and capabilities of the SDKs.
Logging in
API: Marketplace API
Some endpoints require that a user is logged in first, e.g. creating listings, viewing their own listings, or initiating inquiry transactions.
const sharetribeSdk = require('sharetribe-flex-sdk');
var sdk = sharetribeSdk.createInstance({
clientId: '<Client ID>',
});
sdk
.login({ username: '<User email>', password: '<User password>' })
.then((_) => {
// Request dependent on an authenticated user access token
});Initiating a transaction
API: Marketplace API
The process of initiating a transaction is highly variable because it depends entirely on transaction flow customizations and the required parameters of the transition.
For this example, we’ll use the default-booking process, and choose
transition/request-payment as the first step. This requires that:
- The customer is logged in
- A token exchange is made to get a trusted user access token
- The request includes the following parameters
transitionprocessAliasparamslistingIDbookingStartbookingEndlineItems
This example uses the minimum required parameters per the transition defined in the transaction process. You’ll likely want to include more information during this step, e.g. updating the transaction’s extended data. See the Marketplace API reference documentation for more information.
const sharetribeSdk = require('sharetribe-flex-sdk');
const transition = 'transition/request-payment';
const processAlias = 'default-booking/release-1';
const params = {
listingId: '<Listing ID>',
bookingStart: '2025-12-20T22:00:00.000Z',
bookingEnd: '2025-12-21T22:00:00.000Z',
lineItems: [
{
code: 'line-item/night',
unitPrice: {
_sdkType: 'Money',
amount: 5000,
currency: 'EUR',
},
quantity: 1,
includeFor: ['customer', 'provider'],
},
{
code: 'line-item/provider-commission',
unitPrice: {
_sdkType: 'Money',
amount: 5000,
currency: 'EUR',
},
percentage: -13,
includeFor: ['provider'],
},
],
};
const sdk = sharetribeSdk.createInstance({
clientId: '<Client ID>',
clientSecret: '<Client Secret>',
});
sdk
.login({ username: '<User email>', password: '<User password>' })
.then((_) => {
sdk.exchangeToken().then((res) => {
var sdkTrusted = sharetribeSdk.createInstance({
clientId: '<Client ID>',
tokenStore: sharetribeSdk.tokenStore.memoryStore(res.data),
});
// It's useful to first call initiateSpeculative to validate the data and to ensure
// the real request will complete as expected
sdkTrusted.transactions
.initiateSpeculative(
{
transition,
processAlias,
params,
},
{
expand: true,
}
)
.then((speculatedResult) => {
if (speculatedResult.status == 200) {
sdkTrusted.transactions
.initiate({
transition,
processAlias,
params,
})
.then((initiateResult) => {
// initiateResult.data
});
}
});
});
});Keep your application’s Client Secret secure. Never expose it to untrusted devices or applications such as end user browsers or mobile apps.
Transitioning a transaction
API: Marketplace API
This example shows how you can transition a transaction that has already
been initiated. The logged-in user must be a party that is allowed to
perform the transition - either the customer or provider. This can be
checked in the transaction process visualizer in Console, or from the
transaction’s process.edn file.
Not all transitions require the use of a trusted SDK instance. For non-privileged transitions, simply logging in is sufficient. For privileged transitions however, you’ll need to use a trusted SDK instance. You can read more about privileged transitions here .
const sharetribeSdk = require('sharetribe-flex-sdk');
var sdk = sharetribeSdk.createInstance({
clientId: '<Client ID>',
clientSecret: '<Client Secret>',
});
sdk
.login({ username: '<User email>', password: '<User password>' })
.then((_) => {
sdk.exchangeToken().then((res) => {
var sdkTrusted = sharetribeSdk.createInstance({
clientId: '<Client ID>',
tokenStore: sharetribeSdk.tokenStore.memoryStore(res.data),
});
sdkTrusted.transactions
.transition({
id: '<Transaction ID>',
transition: '<Transition name>',
params: {},
})
.then((res) => {
// res.data
});
});
});Updating metadata in a transaction
API: Integration API
Updating metadata for a transaction requires that you use the Integration API.
const integrationSdk = require('sharetribe-flex-integration-sdk');
var sdk = integrationSdk.createInstance({
clientId: '<Client ID>',
clientSecret: '<Client Secret>',
});
sdk.transactions
.updateMetadata({
id: '<Transaction ID>',
metadata: {
'<Key>': '<Value>',
},
})
.then((res) => {
// res.data
});Updating a listing
API: Marketplace API
Updating a listing requires that the listing author’s credentials are used.
const sharetribeSdk = require('sharetribe-flex-sdk');
var sdk = sharetribeSdk.createInstance({
clientId: '<Client ID>',
});
sdk
.login({ username: '<User email>', password: '<User password>' })
.then((_) => {
sdk.ownListings
.update({
id: '<Listing ID>',
description: '<Updated description>',
privateData: {
'<Key>': '<Value>',
},
publicData: {
'<Key>': '<Value>',
},
})
.then((res) => {
// res.data
});
});Retrieving listing assets defined in Console
API: Asset delivery API
This example will show how to retrieve all listing-related configurations as defined in Console.
- Types
- Categories
- Fields
- Search
const sharetribeSdk = require('sharetribe-flex-sdk');
var sdk = sharetribeSdk.createInstance({
clientId: '<Client ID>',
});
sdk
.assetsByAlias({
paths: [
'/listings/listing-types.json',
'/listings/listing-categories.json',
'/listings/listing-fields.json',
'/listings/listing-search.json',
],
alias: 'latest',
})
.then((res) => {
// res.data
});Additional resources
For the complete documentation on the JavaScript SDKs, visit our Github documentation for the Sharetribe SDK and the Integration SDK . There, you’ll find
- Features
- Configuration options
- Additional examples
- How to use the browser or the API Playground (only available for the Sharetribe SDK) for easy testing